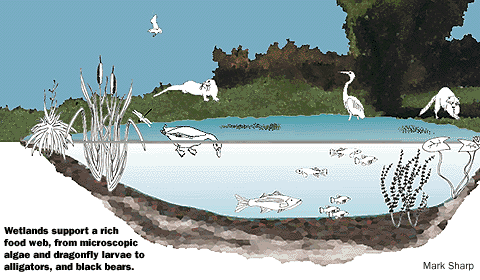
Food chains illustrate the relationship between producers and consumers, showing the different trophic levels in an ecosystem. Because living organisms usually have more than one source of food, these food chains are often linked together, forming food webs. Food webs assist us to identify herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, scavengers, detritivores and decomposers in a community.
Not all relationships within an ecological community are predatory or feeding relationships. Some important relationships are parasitic, mutualistic (both organisms benefit), commensalism (one benefits, the other is not harmed) or parasitism (one benefits and the other is harmed, but usually not killed).
- The Food Chain (4.50min)
- The Food Web (3.07min)
- Aquatic food webs of Kakadu (5.39min)
- Energy transfer in trophic levels (2.41min)
- Symbiotic relationships – Mutualism, commensalism and parasitism.