This Area of Study includes key knowledge about genetics and heredity:
Cell reproduction:
- binary fission in prokaryotes
- the phases of the cell cycle in eukaryotes including DNA replication, the division of the nucleus (mitosis), and cytokinesis
- the key events that result in the production of haploid sex cells from a diploid cell (meiosis), including recombination
Molecular genetics:
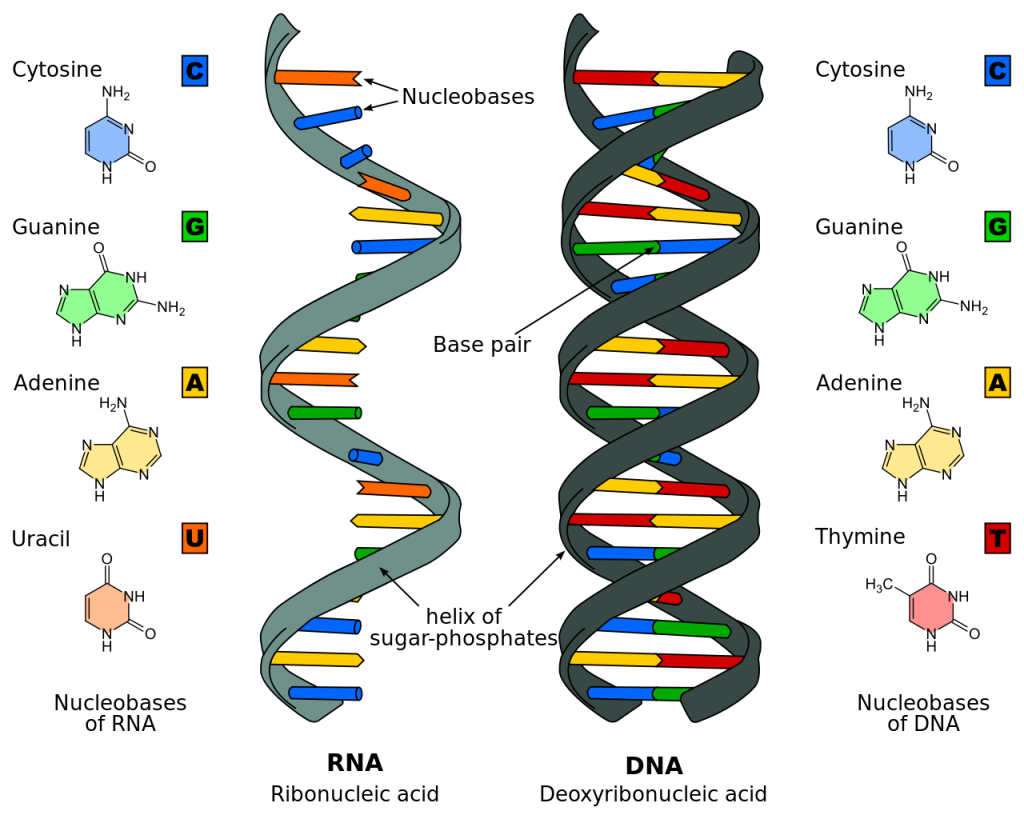
- the nature of genomes, genes and the genetic code
- gene expression: the genetic code and roles of RNA in transcription, RNA processing in eukaryotes, and translation
- the concept of gene regulation (the switching on and off of genes by factors expressed by regulator genes and environmental factors)
DNA tools and techniques:
- gel electrophoresis;
- DNA amplification;
- DNA sequencing;
- making a recombinant plasmid;
- bacterial transformations;
- DNA profiling;
- gene cloning;
- and using plasmids as gene delivery systems
There are a good series of six, (less than) ten-minute videos on YouTube that cover these concepts:
- Gene Technology1 of 6 – Restriction enzymes and ligation
- Gene Technology 2 of 6 – DNA probes and amplification
- Gene Technology 3 of 6 – PCR and gel-electrophoresis
- Gene Technology 4 of 6 – DNA fingerprinting
- Gene Technology 5 of 6 – DNA sequencing
- Gene Technology 6 of 6 – Gene cloning
Inheritance:
- the nature of chromosomes, alleles, genotype and phenotype
- the causes of phenotypic variation: mutations; recombination of parental alleles in sexual reproduction; polygenes; and interactions of environmental factors with genes
- continuous and discontinuous variation
- patterns of inheritance involving the monohybrid cross: dominance; recessiveness; co-dominance; multiple alleles
- dihybrid crosses as independent or linked
- pedigree analysis: autosomal and sex-linked inheritance; use of the test cross.
Some resources to assist your revision of this topic:
- Human Genetics Problem Set from the “University of Arizona – The Biology Project”
- IB Biology Notes – Genetics
- IB Biology – Revision